In India, railway signaling can be classified into two main parts. The part dealing with the motion(and safety)of trains among two stations and the motion(and safety)of trains in the station.
Signaling Blocks and Interlocking
The motion of trains between two stations is administered by a set of rules called the Block Rules. Since there are various types of block working, different rules are applied depending on the type of Block Working which is installed on the section.
Thus, the railway line can broadly be divided into two main parts-the block section and the station section. While the entry of trains into the block section between the stations is governed by the relevant block rules applicable, in the station section, an arrangement called “Interlocking” is provided.
Since the station section will normally have a number of points(the place where a train changes tracks)and signals, it is the interlocking system’s main function to ensure that a conflicting route is not set which might send a train on a collision course with another train!!
Hence, the interlocking system ensures that only the correct signals are cleared for the movement of trains and if a track is already occupied by another train or some other issue prevents the safe movement of the train, the interlocking system ensures that the signal cannot be cleared.
Before the signal for a train is cleared,the interlocking system ensures that all points in the route are set(in required position) and locked, all tracks up to the next signal are clear of any other vehicles and the clearance of the signal will not result in a conflicting route with some other potential or ongoing movement.
Interlocking systems also come in several varieties such as purely mechanical interlocking, hybrid electro-mechanical interlocking, relay-based Panel Interlocking and relay based Route Relay Interlocking. The latest technology being used on the IR is called the Electronic Interlocking, consisting of computerized systems for signaling.
Similarly, there is also various block working system such as Token working on single-lines, Tokenless working on single lines, SGE(Siemens and General Electric) type block working instrument on double lines and the latest being BPAC(Block Proving by Axle Counter)system both for single and double lines.
This is how signaling is divided into Indian railways
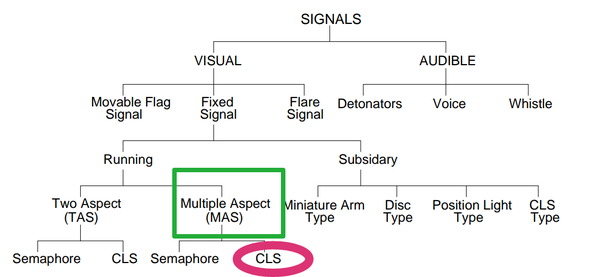
Nowadays Indian railways using Multiple Aspect Color Light Signaling (As made in the above picture)
The train is controlled based on the aspects indicated.
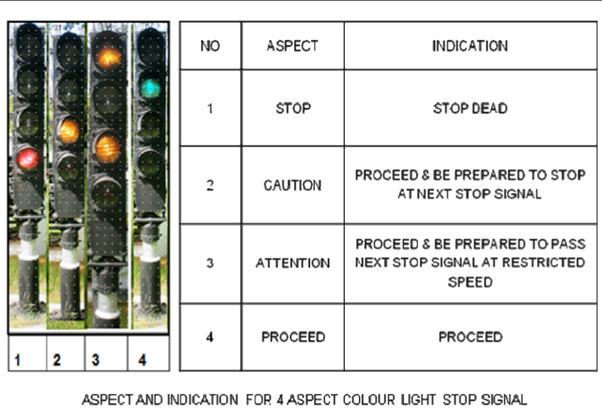
The red is placed at Driver’s eye level, the yellow above it, the green next above it and the second yellow light above the green light. The two yellows are separated by the green to provide a distinctive “Attention” aspect and the double yellow is chosen as the aspect less restrictive than the single yellow, so that should any one of the two yellow lamps be fused, a more restrictive aspect will result.
This is how signaling will be interlocked based on the front signal indications.
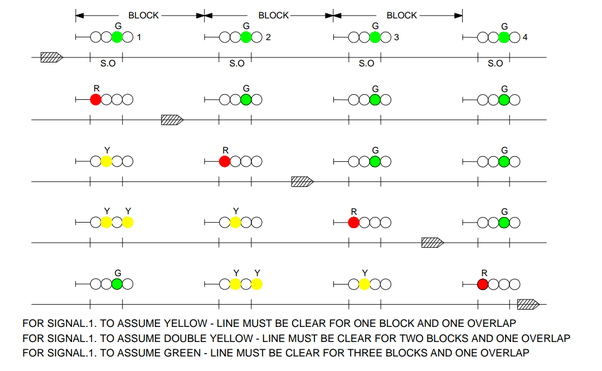
In accordance with the essentials, all running signals protecting the entry of trains into automatic blocks should be replaced to `ON’ automatically. Such signals must not display `yellow’ aspect unless the block and overlap in advance are clear, and a double yellow (or green), unless two blocks in advance and overlap are clear as proved by track circuits. Signals so controlled by track circuit or axle counter are known as Automatic Signals.
Source: Quora

